Fitness for Service Assessment (FSA) and Remaining Life Evaluation (RLE) Services
 Fitness for Service Assessment (FSA) need specific work to inspect the pressure equipment, to evaluate the detected, to identify causes of possible damage of the investigated equipment and, according to that, to determine the remaining life and the necessary repairs or replacements. The main phases of FSA activities shall be as follows:
Fitness for Service Assessment (FSA) need specific work to inspect the pressure equipment, to evaluate the detected, to identify causes of possible damage of the investigated equipment and, according to that, to determine the remaining life and the necessary repairs or replacements. The main phases of FSA activities shall be as follows:
- Elaboration of the FSA program. This document will contain identification of the flaw types and possible damage causes of the investigated pressure equipment, taking account of their design, working parameters, materials, content of processed fluids, technological requirements, operating history. Information related to the Client / Owner of the pressure vessels and pipes or similar cases investigated previously by NNDT will be used for identification of possible flaw types or damage mechanism (known or postulated). On this basis, the necessary examinations and verifications to be performed on the pressure vessels and pipes (Inspection Plan) will be established;
- Performance of examinations and verifications established in the FSA Inspection Plan. The NNDT inspection team will perform the on site inspection work. The necessary material testing for characterization of material damege will be performed in the accredited laboratories of NNDT;
- Analysis of Inspection Data and evaluation of inspection results in respect to the detected or postulated flaws or damage mechanisms. Elaboration of the FSA final report. The final report will contain conclusions if the pressurized equipment containing flaws that have been identified and evaluated by inspection can continue to operate safely for some period of time or not, and recommendations for run – repair – replace decisions. The scope of the final report will cover both, the present integrity of the investigated pressure equipment given a current state of damage and the projected remaining life;
- As separate activity Nuclear NDT can perform the necessary engineering activities to elaborate the repair design documentations and / or pressure equipment surveillance programs.
As reference FSA methodologies, the API standards, ASME Code, European (EN) or ISO standards are usually applied.
Technical Inspection of piping systems, pressure vessels, tanks, and other pressure equipment and or critical components according to ISCIR Technical Prescriptions
 NNDT is currently doing Technical Inspection of pressure vessels, piping systems or tanks for characterization of the technical state, evaluation of structural integrity, and estimation of the remaining life according to applicable ISCIR Technical Prescriptions C1 (Boilers), C4 (Pressure Vessels), C6 (Technological Pipes), C10 (Warm Water & Steam Pipes), …..
NNDT is currently doing Technical Inspection of pressure vessels, piping systems or tanks for characterization of the technical state, evaluation of structural integrity, and estimation of the remaining life according to applicable ISCIR Technical Prescriptions C1 (Boilers), C4 (Pressure Vessels), C6 (Technological Pipes), C10 (Warm Water & Steam Pipes), …..
According to Romanian legislation, the Technical Inspection is required for various purposes, as specified below:
- Technical Inspection is required as basic support for obtaining ISCIR operation permit (authorization) of pressure vessels and piping systems with consumed design life or affected by accidents / integrity events;
- Technical Inspection is required when ISCIR recording of pressure equipment (most often, piping systems) according to applicable ISCIR prescription C1, C4, C6,… and C10 is necessary if the equipment was not previously (not yet) recorded;
- Failure analysis of pressure equipment or various pressure boundary critical components, in order to establish the root causes of failure events and to establish corrective actions to prevent failure.
Technical Inspection is performed according to an investigation program based on various testing and examination methods (destructive – in our specific laboratories on samples taken from the investigated systems, or non destructive – by site inspections using appropriate methods. When it is possible, high temperature examinations during operation is performed in order to save the plant capacity factor. Also, computer modeling, including Finite Element Analysis, are performed in order to simulate the thermo – mechanical behavior of the investigated components and systems.
As the TechnicalInspection is performed following ISCIR requirements, the investigation programs are elaborated and subjected to ISCIR approvals according to the specific technical prescriptions. Evaluation of the remaining life is a compulsory requirement of the Technical Inspection.
Design Engineering activities and elaboration of repair documentations
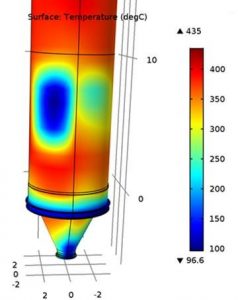
 This activities consists of elaboration of design solutions and of repair design documentations for piping systems and pressure vessels, according to ISCIR requirements. Our design engineers are authorized by ISCIR for verification and final approval of repairs design documentation.
This activities consists of elaboration of design solutions and of repair design documentations for piping systems and pressure vessels, according to ISCIR requirements. Our design engineers are authorized by ISCIR for verification and final approval of repairs design documentation.
Design engineering covers, also, various activities like:
- Elaboration of piping lines isometric drawings in electronic format;
- Piping flexibility calculations;
- Elaboration of assembly drawings of pressure equipment;
- Elaboration of design calculus for piping systems and pressure vessels, including the case when the design parameters are changed;
- Stress Analysis by Finite Element Methodology.
Elaboration and Implementation of Pressure Equipment Surveillance Programs based on Risk Evaluations
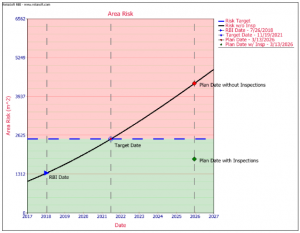 When it is requested, risk evaluations to known and postulated failure events are performed, in order to prevent major failures and to optimize the inspection programs of critical systems, equipments, and components.
When it is requested, risk evaluations to known and postulated failure events are performed, in order to prevent major failures and to optimize the inspection programs of critical systems, equipments, and components.
The critical technological & safety piping lines and pressure vessels behaviour is modeled by specialized software codes for:
- Optimal selection of inspection zones;
- Real – Time Estimation of the erosion / corrosion degradation rate and remaining life (consequence: deep decrease of the failure probability);
- Determination of the optimal inspection intervals.
Through its Research & Development department and based on its field experience, NNDT continuously improve the numerical modeling capability in order to permanently increase the reliability of the risk evaluations.
